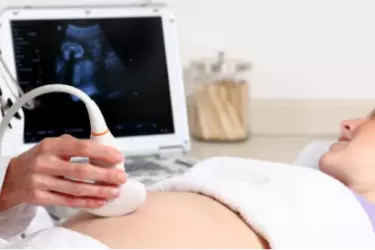
Ultrasound involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to create images of organs and systems within the body. An ultrasound machine creates images that allows various organs in the body to be examined. The machine sends out high-frequency sound waves, which reflect off body structures. The transducer has receptors which receive these signals and convert them into digital signals and form image of the body organ on the computer screen. Ultrasound is the gold standard for looking at the health of foetus in pregnant women. It allows the gynaecologists to detect any congenital abnormalties in the foetus and take corrective action
Ultrasound is extremely useful in diagnosing diseases of the organs in the abdomen, blood vessels and soft tissues. The best thing about ultrasound exam is that it is completely harmless and involves no radiation unlike other diagnostic modalities like X-Ray, CT Scan, Mammography etc.
At Bharat Diagnostics Bhiwadi we have the latest and most advanced 4-D Ultrasound machine. We have the first 4-D Transvaginal and Transrectal Transducer which is extremely useful in diagnosing diseases of Uterus and Prostate. Transvaginal ultrasound is an internal ultrasound. It involves scanning with the ultrasound probe lying in the vagina. Transvaginal ultrasound usually produces better and clearer images of the female pelvic organs, because the ultrasound probe lies closer to these structures. The female patients would usually prefer a female radiologist to perform the Transvaginal or TVS Studies.
3D/4D ultrasound can obtain views of the pelvis that are not seen on the conventional 2D ultrasound, especially views of the uterus. 2D ultrasound can obtain longitudinal and transverse views of the uterus. 3D ultrasound adds in the coronal view (or C-plane) of the uterus, enabling us to get an image of the uterus that is “front on”.
3D/4D ultrasound may help in the diagnosis and assessment of pelvic conditions, including:
![]() Congenital uterine abnormalities. Some women are born with changes in the shape of the uterus (for example, bicornuate uterus). Minor changes in the shape of the uterus are not uncommon.
Congenital uterine abnormalities. Some women are born with changes in the shape of the uterus (for example, bicornuate uterus). Minor changes in the shape of the uterus are not uncommon.
![]() The location of endometrial polyps.
The location of endometrial polyps.
![]() The location of submucous fibroids and assessment of any intramural component.
The location of submucous fibroids and assessment of any intramural component.
![]() The location of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD), especially if the IUCD is abnormally located (for example, penetrating into the wall of the uterus).
The location of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD), especially if the IUCD is abnormally located (for example, penetrating into the wall of the uterus).
![]() Investigation of recurrent miscarriages and preterm deliveries.
Investigation of recurrent miscarriages and preterm deliveries.
The cost of Ultrasound depends upon the type. It ranges from INR 1000 to INR 3000 depending upon the scan type.
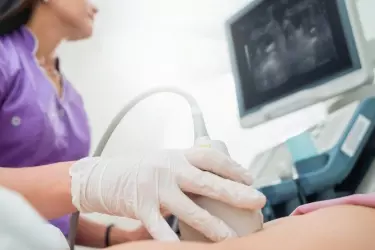
Pregnancy Ultrasound - In order to measure the growth of the foetus, ultrasound is the only diagnostic modality. During the nine months of the pregancy atleast 3 ultrasound exams are done, one in every trimester. In the first ultrasound of the pregnancy the viability of the foetus is determined alongwith foetal heart rate and the gestational age. This ultrasound also gives the expected date of delivery.
During the second trimester around 14-15 weeks of pregnancy a very detailed and indepth ultrasound is done called Level II Scan which gives complete information about the congenital abnormalities in the foetus.
![]() Testicle ultrasound
Testicle ultrasound
![]() Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound
![]() Transvaginal ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound
![]() Vascular ultrasound
Vascular ultrasound

Dr Rajesh Choudhary has more than 20 years of experience in the field of Radiology. Dr Choudhary has been trained in the latest radiological techniques from Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner and PGI Chandigarh.

Dr Shruti Sangwan has been trained at Lady Hardinge Medical College, Maulana Azad Medical College, PGI Chandigarh and Artemis Hospital Bhiwadi in the field of Radiology and has more than 18 years of experience.


