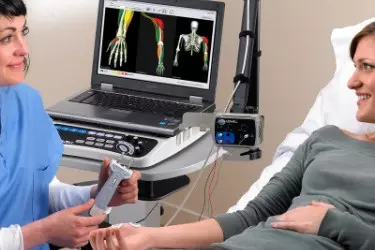
Nerve Conduction Velocity Study (NCV) is a test commonly done to evaluate the function, especially the ability of electrical conduction of the motor and sensory nerves of the human body. Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a common measurement made during this test. Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
In cases of injury to the arm or the legs these nerves can get damaged and their capacity to carry electrical signals get reduced. In patients who consume a lot of alcohol or diabetic patients these nerves age much faster and their functioning becomes less effective which causes numbness or tingling sensations in the fingers of the hands or the legs.
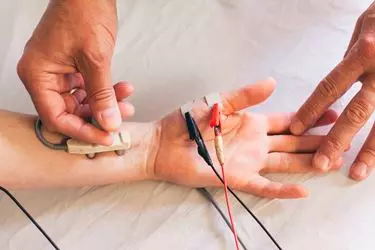
During the test, the nerve is stimulated, usually with surface electrode patches attached to the skin. Two electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerve. One electrode stimulates the nerve with a very mild electrical impulse and the other electrode records it. The resulting electrical activity is recorded by another electrode. This is repeated for each nerve being tested.
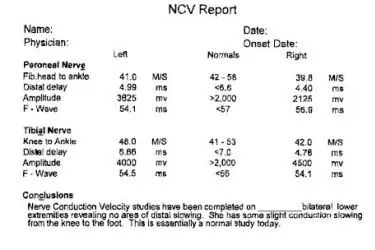
The nerve conduction velocity (speed) is then calculated by measuring the distance between electrodes and the time it takes for electrical impulses to travel between electrodes.
Conditions that may be evaluated with NCV include the following:
![]() Guillain-Barré syndrome - A condition in which the body's immune system attacks part of the peripheral nervous system. The first symptoms may include weakness or tingling sensations in the legs.
Guillain-Barré syndrome - A condition in which the body's immune system attacks part of the peripheral nervous system. The first symptoms may include weakness or tingling sensations in the legs.
![]() Carpal tunnel syndrome - A condition in which the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist by enlarged tendons or ligaments. This results in pain and numbness in the fingers.
Carpal tunnel syndrome - A condition in which the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist by enlarged tendons or ligaments. This results in pain and numbness in the fingers.
![]() Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease - A hereditary neurological condition that affects both the motor and sensory nerves. One characteristic is weakness of the foot and lower leg muscles.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease - A hereditary neurological condition that affects both the motor and sensory nerves. One characteristic is weakness of the foot and lower leg muscles.
![]() Herniated disk disease
Herniated disk disease
![]() Chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy and neuropathy - These are conditions resulting from diabetes or alcoholism.
Chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy and neuropathy - These are conditions resulting from diabetes or alcoholism.
![]() Sciatic nerve problems
Sciatic nerve problems
![]() Peripheral nerve injury
Peripheral nerve injury
![]() Nerve conduction studies may also be performed to identify the cause of symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and continuous pain.
Nerve conduction studies may also be performed to identify the cause of symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and continuous pain.
You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
Generally, no fasting or sedation is required prior to the procedure. Normal body temperature must be maintained before and during the procedure, as low body temperature slows nerve conduction. Notify your doctor of all medications (prescribed and over-the-counter) and herbal supplements that you are taking. Also tell your doctor if you have a cardiac defibrillator or pacemaker, as precautions may need to be taken. Stop using lotions or oils on your skin for a few days before your procedure.
During the test when the electrical impulse is given to the electrode you may feel like a mild electric tingling. Depending on how strong the stimulus is, you will feel it to varying degrees, and it may be slightly uncomfortable. You should feel no pain once the test is finished.
The test is normally done by a technician and the reports are analyzed by a neurologist. Most of the diagnostic centres normally do not have the facility of NCV testing because of the unavailability of the Neurologist. It is best to call up a diagnostic centre to find out the availability of the test and the charges.

Dr Rajesh Choudhary has more than 20 years of experience in the field of Radiology. Dr Choudhary has been trained in the latest radiological techniques from Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner and PGI Chandigarh.

Dr Shruti Sangwan has been trained at Lady Hardinge Medical College, Maulana Azad Medical College, PGI Chandigarh and Artemis Hospital Bhiwadi in the field of Radiology and has more than 18 years of experience.


